Ultimate Guide to Hybrid Cloud Services: Transforming Business Operations in 2025
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, hybrid cloud services have emerged as the cornerstone of enterprise transformation, enabling organizations to leverage the best of both public and private cloud environments. As businesses increasingly demand flexibility, security, and scalability, hybrid cloud solutions offer the perfect balance to meet diverse operational requirements while optimizing costs and performance.
Table of Contents
What Are Hybrid Cloud Services?
Key Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Services
Essential Components of Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Hybrid Cloud vs Public vs Private Cloud
Implementation Strategies for Hybrid Cloud Services
Industry Use Cases and Applications
Security Considerations in Hybrid Cloud Environments
Choosing the Right Hybrid Cloud Services Provider
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud Technology
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Hybrid Cloud Services?
Hybrid cloud services represent a computing environment that seamlessly combines public cloud resources with private cloud infrastructure and on-premises systems. This integrated approach allows organizations to maintain sensitive data and critical applications in private environments while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public cloud services for less sensitive workloads.
The hybrid model enables businesses to move data and applications between different cloud environments as computing needs and costs change, providing greater flexibility and more deployment options. Modern hybrid cloud architectures incorporate advanced AI and automation technologies to optimize resource allocation and enhance operational efficiency.
Key Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Services
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability
Organizations can scale computing resources up or down based on demand without overcommitting to expensive infrastructure. This elasticity ensures optimal resource utilization while maintaining performance during peak periods.
Improved Security and Compliance
Sensitive data and regulated workloads remain in secure private environments while non-critical applications leverage public cloud benefits. This approach helps organizations meet strict compliance requirements in industries like healthcare, finance, and government.
Cost Optimization
By strategically placing workloads based on performance requirements and cost considerations, businesses can significantly reduce operational expenses. Public clouds handle variable workloads cost-effectively while private infrastructure manages predictable, steady-state operations.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Hybrid architectures provide robust backup and recovery options across multiple environments, ensuring business continuity even during system failures or natural disasters.
Innovation Acceleration
Access to cutting-edge public cloud services like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and analytics tools enables rapid innovation without significant upfront investments in specialized infrastructure.
Essential Components of Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Cloud Management Platform
A centralized management console provides unified visibility and control across all cloud environments, enabling consistent policy enforcement and resource optimization.
Network Connectivity Solutions
Secure, high-performance connections between cloud environments ensure seamless data flow and application communication. This includes VPN connections, dedicated circuits, and software-defined networking solutions.
Identity and Access Management
Integrated security frameworks maintain consistent user authentication and authorization across all environments while protecting against unauthorized access.
Data Integration and Migration Tools
Specialized tools facilitate smooth data movement between environments while maintaining data integrity and minimizing downtime during migrations.
Monitoring and Analytics Platforms
Comprehensive monitoring solutions provide real-time insights into performance, security, and resource utilization across the entire hybrid infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud vs Public vs Private Cloud
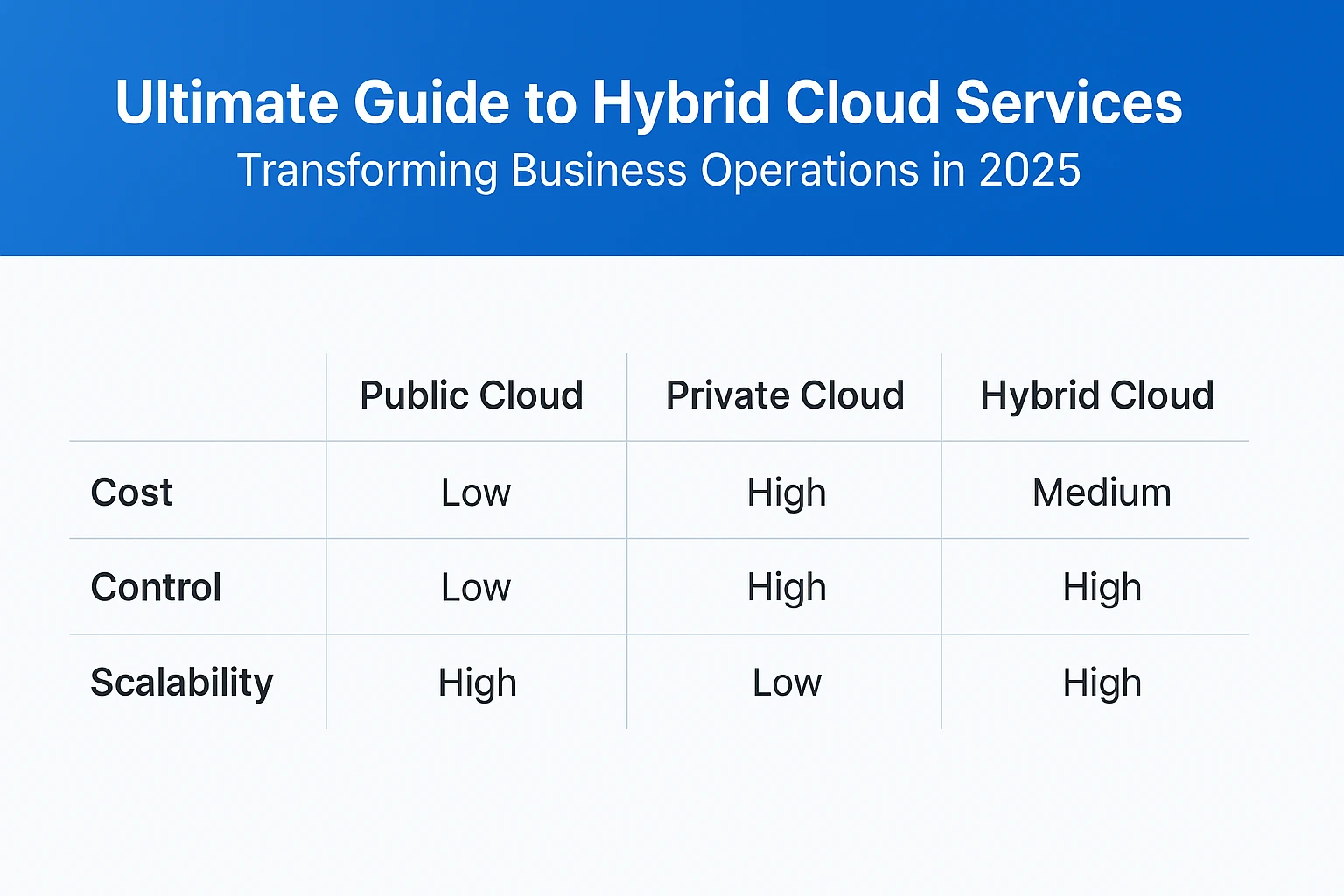
Understanding the differences between cloud deployment models helps organizations make informed decisions:
Public Cloud: Shared infrastructure managed by third-party providers, offering cost-effectiveness and rapid scalability but with limited customization and control.
Private Cloud: Dedicated infrastructure providing maximum security and control but requiring significant upfront investment and ongoing management.
Hybrid Cloud: Combines both models, allowing organizations to optimize workload placement based on specific requirements while maintaining flexibility and control.
The hybrid approach enables strategic workload distribution, placing mission-critical applications in private environments while leveraging public cloud services for development, testing, and variable workloads.
Implementation Strategies for Hybrid Cloud Services
Assessment and Planning Phase
Conduct thorough assessments of existing infrastructure, applications, and business requirements. Identify which workloads benefit from public cloud migration and which should remain in private environments.
Phased Migration Approach
Implement hybrid cloud solutions gradually, starting with non-critical applications to gain experience and refine processes before migrating essential business systems.
Integration and Orchestration
Establish seamless connectivity between environments and implement orchestration tools to automate resource provisioning and management across the hybrid infrastructure. This often involves DevOps automation services to streamline deployment processes.
Security Framework Implementation
Deploy consistent security policies and controls across all environments, ensuring data protection and regulatory compliance throughout the hybrid ecosystem.
Performance Optimization
Continuously monitor and optimize resource allocation, network performance, and application responsiveness to maximize the benefits of hybrid cloud deployment.
Industry Use Cases and Applications

Healthcare Organizations
Medical institutions use hybrid clouds to maintain patient data in HIPAA-compliant private environments while leveraging public cloud services for research, analytics, and non-sensitive applications.
Financial Services
Banks and financial institutions keep critical transaction systems and customer data in secure private clouds while using public clouds for customer-facing applications and analytics workloads.
Manufacturing Companies
Manufacturers maintain production control systems on-premises while utilizing public cloud services for supply chain management, customer relationship management, and business intelligence applications. Many benefit from application modernization services to optimize their hybrid deployments.
Government Agencies
Public sector organizations balance security requirements with cost-effectiveness by keeping classified information in private environments while using public clouds for citizen services and non-sensitive operations.
Security Considerations in Hybrid Cloud Environments

Data Protection Strategies
Implement encryption for data at rest and in transit across all environments. Establish clear data classification policies to ensure appropriate protection levels for different information types.
Network Security Measures
Deploy firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure connectivity solutions to protect data flows between cloud environments and prevent unauthorized access.
Compliance Management
Maintain consistent compliance postures across all environments by implementing automated policy enforcement and regular audit procedures.
Identity Governance
Establish centralized identity management systems that provide secure access control while maintaining user experience across hybrid environments.
Choosing the Right Hybrid Cloud Services Provider
Technical Expertise and Experience
Evaluate providers based on their track record in designing and implementing hybrid cloud solutions across various industries and use cases.
Integration Capabilities
Assess the provider's ability to seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure and support diverse technology stacks and platforms.
Security and Compliance Credentials
Verify provider certifications and compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations that apply to your organization.
Support and Service Quality
Consider the level of ongoing support, monitoring, and optimization services provided to ensure long-term success of your hybrid cloud implementation. Look for providers offering comprehensive enterprise support services to maintain optimal performance.
Innovation and Technology Roadmap
Choose providers that demonstrate commitment to emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation to future-proof your investment. Digital transformation engineering services can help align your hybrid cloud strategy with broader business transformation goals.
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud Technology
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI-powered automation will increasingly optimize resource allocation, predict performance issues, and enhance security across hybrid environments.
Edge Computing Convergence
Integration of edge computing capabilities will extend hybrid cloud benefits to remote locations and Internet of Things deployments.
Serverless Architecture Adoption
Serverless computing models will simplify application deployment and management across hybrid environments while reducing operational overhead.
Enhanced Multi-Cloud Management
Advanced orchestration platforms will provide even greater flexibility in managing workloads across multiple cloud providers and deployment models.
Quantum-Safe Security
Implementation of quantum-resistant encryption and security measures will ensure long-term data protection as quantum computing technologies evolve.
Transform Your Business with Professional Hybrid Cloud Services
Hybrid cloud services represent the future of enterprise computing, offering the perfect balance of flexibility, security, and cost-effectiveness. By strategically combining public and private cloud resources with on-premises infrastructure, organizations can optimize their operations while maintaining control over sensitive data and critical applications.
The key to successful hybrid cloud implementation lies in choosing the right partner who understands your unique business requirements and can design tailored solutions that drive growth and innovation. With proper planning, implementation, and ongoing optimization, hybrid cloud services can transform your organization's capabilities and competitive position in the digital marketplace.
Ready to embark on your hybrid cloud transformation journey? Partner with experienced professionals who can guide you through every step of the process, from initial assessment to ongoing optimization and support.
Ready to transform your business with cutting-edge hybrid cloud solutions? Contact our experts today to discover how IdeaGCS can help you design and implement a hybrid cloud strategy that drives innovation, enhances security, and optimizes costs for your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a hybrid cloud example?
What are the disadvantages of hybrid cloud?
How to build a hybrid cloud?
Is AWS a hybrid cloud?
What is the difference between hybrid cloud and multi-cloud?
Is Azure a hybrid cloud?
What are AWS hybrid cloud services?
What are the 4 types of cloud computing?
Is hybrid cloud scalable?
What is Microsoft Cloud vs Azure?
Contact Us
Share on Social Media
Contact Us
